摘要
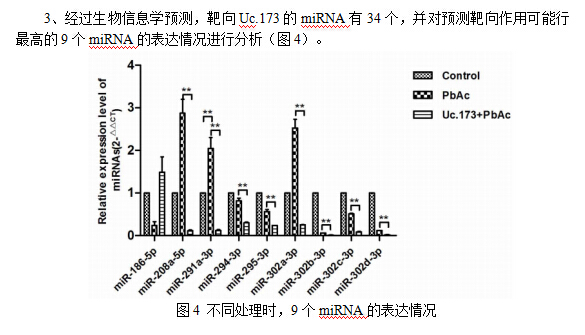
As a common toxic metal, lead has significant neurotoxicity to brain development. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) function in multiple biological processes. However, whether lncRNAs are involved in lead-induced neurotoxicity remains unclear. Uc.173 is a lncRNA from a transcribed ultra-conservative region (T-UCR) of human, mouse and rat genomes. We established a lead-induced nerve injury mouse model. It showed the levels of Uc.173 decreased significantly in hippocampus tissue and serum of the model. We further tested the expression of Uc.173 in serum of lead-exposed children, which also showed a tendency to decrease. To explore the effects of Uc.173 on leadinduced nerve injury, we overexpressed Uc.173 in an N2a mouse nerve cell line and found Uc.173 had an inhibitory effect on lead-induced apoptosis of N2a. To investigate the molecular mechanisms of Uc.173 in apoptosis associated with lead-induced nerve injury, we predicted the target microRNAs of Uc.173 by using miRanda, TargetScan and RegRNA. After performing quantitative real-time PCR and bioinformatics analysis, we showed Uc.173 might inter-regulate with miR-291a-3p in lead-induced apoptosis and regulate apoptosis-associated genes. Our study suggests Uc.173 significantly inhibits the apoptosis of nerve cells, which may be mediated by inter-regulation with miRNAs in lead-induced nerve injury.
研究背景
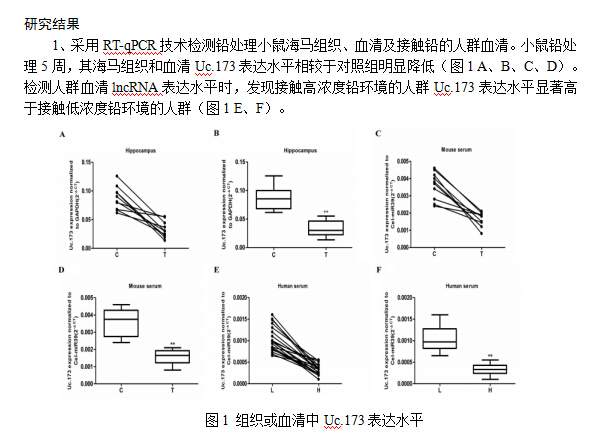
金属铅中毒在人群中已造成重大危害,尤其是在儿童群体中,研究表明,铅作为一种神经发育性强烈毒药。铅中毒将会导致神经性坏死。近年来,多项研究表明lncRNA在外源性致癌中发挥重要作用,但是在铅致神经损伤方面未见报道。研究表明,一些转录的超保守基因,如Uc.73 和 Uc.338能作为肿瘤蛋白促进癌细胞生长。通过lncRNA芯片分析,发现超保守lncRNA Uc.173表达水平随着靶基因的变化而变化。为了研究在铅致神经损伤中 Uc.173发挥的作用,本文在小鼠脑组织、血清过表达Uc.173,并检测该组织中lncRNA的表达情况,同时,检测接触铅的人类血清。利用小鼠神经细胞N2a进一步探究Uc.173在铅致神经性凋亡中发挥的作用。
方法流程
伯信合作技术
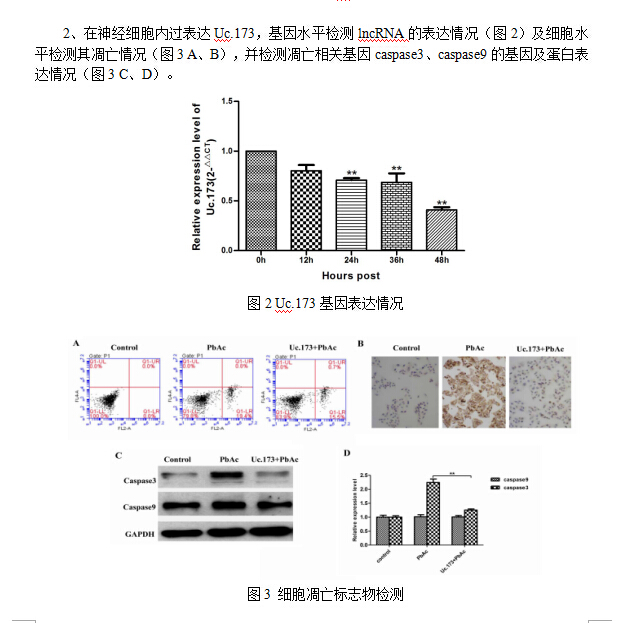
lncRNA过表达载体的构建、TUNEL。
参考文献
Nan A, Zhou X, Chen L, et al. A transcribed ultraconserved noncoding RNA, Uc.173, is a key molecule for the inhibition of lead-induced neuronal apoptosis[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 7(1):112-124.
原文链接




