伯信生物建立了地高辛原位杂交探针(ISH Probe)制备平台,承接定制地高辛原位杂交试剂盒业务,可根据客户需要进行个性化定制。该试剂盒主要用于检测样本中目的基因的表达量及表达位置,可用于组织切片(石蜡切片/冰冻切片)、细胞爬片、染色体片等的检测。 (本试剂盒仅供科研用途)
伯信生物建立了地高辛原位杂交探针(ISH Probe)制备平台,承接定制地高辛原位杂交试剂盒业务,可根据客户需要进行个性化定制。该试剂盒主要用于检测样本中目的基因的表达量及表达位置,可用于组织切片(石蜡切片/冰冻切片)、细胞爬片及染色体片等的检测。
伯信生物地高辛原位杂交试剂盒,自上市以来深受广大科研用户的欢迎和肯定,为中国科学院、中山大学医学院及附属医院、南方医科大学医学院及附属医院、香港大学、北京大学医学部及附属医院、东南大学医学院、江西农业大学、华中科技大学同济医学院等国内一流科研院所、医疗机构及跨国生物企业等近千家用户提供了优质的服务。同时经过多年的积累,伯信生物拥有强大的原位杂交技术团队,为客户在试剂盒使用中遇到的各种问题给予技术支持和解答。
目前公司拥有库存现货试剂盒种类已达近千种:其中mRNA 约1100种;microRNA 约 500种;种属涵盖人、大小鼠、兔、猪、鸡、细菌、昆虫类等等。
实验原理:
显色原位杂交技术(Chromogenic in situ hybridization, CISH)是根据待测核酸序列设计特异性的末端标记寡聚核苷酸探针,再经过共变性-退火-复性,使探针与靶DNA/RNA按照碱基互补配对原则形成杂交体,最后利用光学显微镜检测杂交信号,从而对组织、细胞中的待测核酸进行定性、半定量或相对定位分析的一种原位杂交技术。
技术流程:
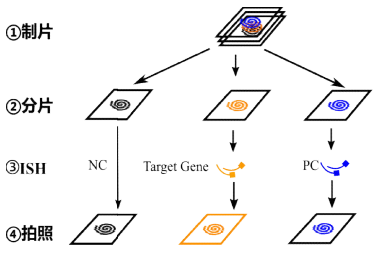
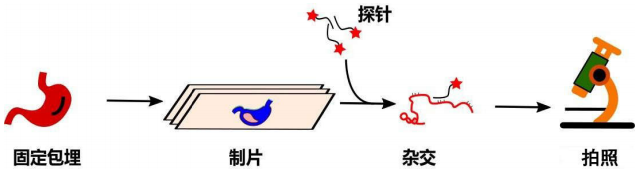
结果实例:

产品优势:
1. 信号清晰,定位准确,结果判定直观可靠。
2. 根据客户需求定制个性化探针。
3. 特异性强,灵敏度高,背景低。
4. 探针性能稳定,低温保存一年以上。
5. 操作简单,安全、快速,重复性好。
文章案例
【2025年】
Article:Effect of miR-6767-5p on breast cancer cell phenotype and its regulatory mechanism.
Periodicals:Scientific Reports
IF:3.900
Periodicals:European Journal of Histochemistry: EJH
IF:2.100
【2023年】
Periodicals:Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research
IF:11.300
Periodicals:Translational Oncology
IF:5.002
Article:Role of LncRNA MIR99AHG in breast cancer: Bioinformatic analysis and preliminary verification
Periodicals:Heliyon
IF:4.000
【2022年】
Periodicals:Cancer Science
IF:5.700
Periodicals:European Journal of Histochemistry
IF:2.000
【2020年】
Article:An NF-κB–driven lncRNA orchestrates colitis and circadian clock
Periodicals:SCIENCE ADVANCES
IF:13.600
Article:MiR-4310 induced by SP1 targets PTEN to promote glioma progression
Periodicals:Cancer Cell International
IF:5.800
Periodicals:Molecular Medicine Reports
IF:3.400
【2019年】
Periodicals:NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
IF:12.122
Periodicals:Theranostics
IF:8.698
Periodicals:Molecular Therapy
IF:7.97
Periodicals:Molecular Oncology
IF:6.570
Article:Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote PD-L1 expression in mice cancer cells via secreting CXCL5
Periodicals:International Journal of Cancer
IF:6.4
【2018年】
Periodicals:Cell Death & Disease
IF:5.638
Periodicals:Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
IF:2.62
【2017年】
Article:OCT4B1 Regulates the Cellular Stress Response of Human Dental Pulp Cells with Inflammation
Periodicals:BioMed Research International
IF:2.583
【2016年】
Periodicals:NATURE COMMUNICATIONS
IF:12.353
Periodicals:Cancer Letters
IF:6.491