
摘要
As a common female malignancy, triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most serious subtype in breast cancer (BC). BAALC binder of MAP3K1 and KLF4 (BAALC) is a common oncogene in acute myelocytic leukemia (AML). We sought to explore the role of BAALC in TNBC. In this study, BAALC was significantly upregulated in TNBC tissues and cells. Then, the results of functional assays disclosed that BAALC facilitated cell proliferation, invasion, and epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) processes, but repressed cell apoptosis in TNBC. Next, miR-380–3p was identified as the upstream of BAALC in TNBC cells. Moreover, LRRC75A-AS1 (also named small nucleolar RNA host gene 29: SNHG29) was verified to act as the sponge of miR-380–3p to elevate BAALC expression in TNBC. Besides, LRRC75A-AS1 could negatively regulate miR-380–3p but positively regulate BAALC expression. Finally, rescue assays elucidated that LRRC75A-AS1 facilitated cell proliferation, invasion, and EMT processes in TNBC by targeting miR- 380–3p/BAALC pathway. Taken together, our study revealed a novel ceRNA network of LRRC75A-AS1/miR-380–3p/ BAALC in accelerating TNBC development, indicating new promising targets for TNBC treatment.
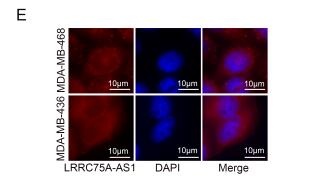
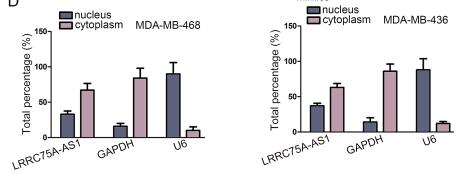
伯信合作技术:FISH探针




