
摘要
The genetic determination of eggshell coloration has not been determined in birds. Here we report that the blue eggshell is caused by an EAV-HP insertion that promotes the expression of SLCO1B3 gene in the uterus (shell gland) of the oviduct in chicken. In this study, the genetic map location of the blue eggshell gene was refined by linkage analysis in an F2 chicken population, and four candidate genes within the refined interval were subsequently tested for their expression levels in the shell gland of the uterus from blue-shelled and non-blue-shelled hens. SLCO1B3 gene was found to be the only one expressed in the uterus of blue-shelled hens but not in that of non-blue-shelled hens. Results from a pyrosequencing analysis showed that only the allele of SLCO1B3 from blue-shelled chickens was expressed in the uterus of heterozygous hens (O*LC/O*N). SLCO1B3 gene belongs to the organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) family; and the OATPs, functioning as membrane transporters, have been reported for the transportation of amphipathic organic compounds, including bile salt in mammals. We subsequently resequenced the whole genomic region of SLCO1B3 and discovered an EAV-HP insertion in the 59 flanking region of SLCO1B3. The EAV-HP insertion was found closely associated with blue eggshell phenotype following complete Mendelian segregation. In situ hybridization also demonstrated that the blue eggshell is associated with ectopic expression of SLCO1B3 in shell glands of uterus. Our finding strongly suggests that the EAV-HP insertion is the causative mutation for the blue eggshell phenotype. The insertion was also found in another Chinese blueshelled breed and an American blue-shelled breed. In addition, we found that the insertion site in the blue-shelled chickens from Araucana is different from that in Chinese breeds, which implied independent integration events in the blue-shelled chickens from the two continents, providing a parallel evolutionary example at the molecular level.
关键词:EAV-HP嵌入物;SLCO1B3基因;焦磷酸测序;蓝蛋壳显性;
研究背景
鸡蛋中两种比较主要的蛋壳色是褐色和白色,而原卟啉、胆绿素、胆绿素锌螯合物是蛋壳的主要色素,其他个别的蓝色蛋品种已经被报导过了。一种智利的阿劳肯鸡是首先被发现蓝色蛋的品种,并在蓝色蛋壳显性遗传学中被频繁引用。在阿劳肯鸡的遗传显性基因中,中国的东乡鸡和卢氏鸡的蓝色蛋是典型品种,然而,在这三种鸟中,蓝色蛋的显性不是固定出现的,也会偶尔出现褐色的蛋。
蓝色蛋壳的颜色出现是由于一个正常染色体的显性遗传以及蛋在异形结合体中,暗蓝色的同形结合体比其他多。1933年,Punnett率先报导了有关阿劳肯鸡中出现蓝色或绿色蛋的是由单个遗传因子所决定的,通常表示为蛋壳青素。包括蛋壳青素在内的一系列关联分析已经确定蛋壳青素的执行是因为染色体1的缺乏,以及与辨别SRγ (性别决定区域γ)-box 5 (SOX5)的ev1和P密切相关。我们发现蓝蛋壳的显性和在ev1周围区域的两个单独多肽核苷酸(SNPs)(rs15297163和rs15297165)有高度的相关性。
方法流程:

研究结果:
利用荧光显微镜成像检测6只异形结合体的蓝色蛋壳鸟类的子宫和肝脏的荧光表达。5’-AACTCTGGCTGAACGCATCT-3’的 cDNA探针被6-FAM标记。
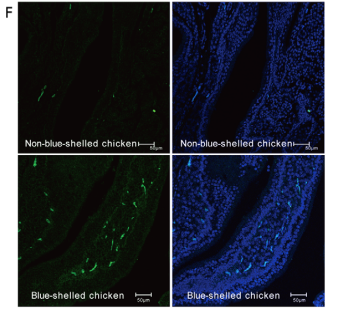
伯信合作技术:荧光杂交技术
参考文献
Wang Z, Qu L, Yao J, et al. An, EAV-HP, Insertion in 5′ Flanking Region of, SLCO1B3, Causes Blue Eggshell in the Chicken[J]. Plos Genetics, 2013, 9(1).
原文链接




