
摘要
Meningitic Escherichia coli invasion of the host brain can lead to increased blood-brain barrier (BBB) permeability. Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are non-coding RNAs, highly abundant in the brain that are widely involved in the pathological processes of central nervous system (CNS) disorders; however, whether circRNAs participate in the regulation of BBB permeability during E. coli meningitis remains unknown. Here, we identified a novel circRNA, circ_2858, that was significantly upregulated in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (hBMECs) upon meningitic E. coli infection. We also found that circ_2858 regulated BBB permeability in hBMECs by competitively binding miR-93-5p, thereby inducing the upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor A and finally resulting in downregulation as well as altered distribution of tight junction proteins such as ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin-5. These findings provide novel insights into the influence of circ_2858 on BBB permeability during the pathogenic process of E. coli meningitis, suggesting potential nucleic acid targets for future prevention and therapy of CNS infection induced by meningitic E. coli .
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier, Brain microvascular endothelial cells, circ_2858, miR-93-5p, V ascular endothelial growth factor A, Permeability
合作部分结果:
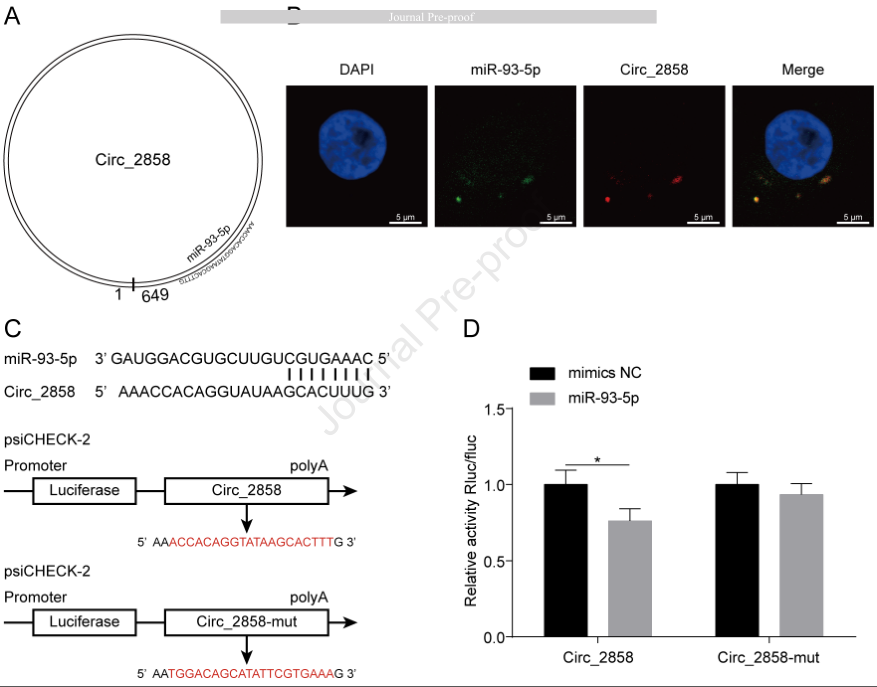

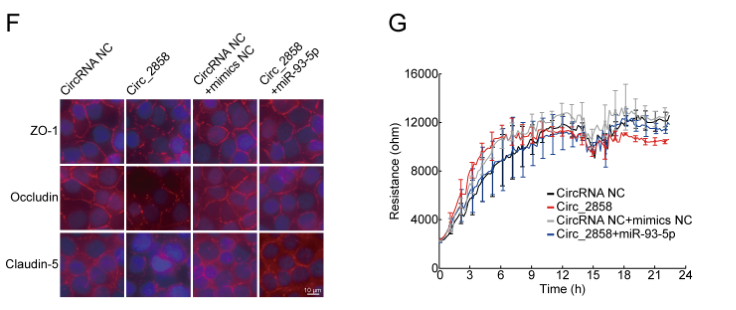
伯信合作技术:circRNA FISH 探针、过表达载体
原文链接: DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.034




