
摘要
Background: Dysregulation of fatty acid (FA) metabolism is involved in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) development. Non-POU domain-containing octamer binding protein (NONO), known as the component of nuclear paraspeckles, has recently been found to promote HCC progression. In this study, we investigated the functions of NONO in regulating de novo FA synthesis and its underling mechanism during HCC development.
Methods: The roles of NONO in HCC development by applying gene function loss analysis in HCC cells were detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, cell proliferation, and cell invasion assays. The underlying mechanism of NONO in HCC development was examined by western blotting, subcellular fractionation, RNA-binding protein immunoprecipitation-sequencing, chromatin immunoprecipitation, co-immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry. The effect of NONO on tumorigenesis in vivo was performed with a subcutaneous xenograft mouse model of HCC.
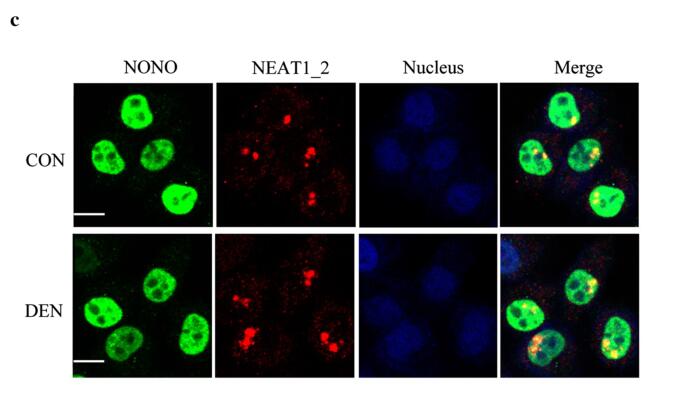
Results: NONO promotes HCC progression by interacting with and increasing ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY) mRNA to enhance FA biosynthesis. Furthermore, NONO promotes ACLY expression through enhancing nuclear ACLY mRNA stability in Diethylnitrosamine-stimulated HCC cells, not related to nuclear paraspeckles. Moreover, we find that NONO/SFPQ (Splicing factor proline and glutamine rich) heterodimer is essential for NONO interacting with ACLY mRNA in DEN stimulated HCC cells. In addition, NONO, Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) and ACLY expressions contribute HCC development in mice and are related to poor survival.
Conclusion: NONO promotes HCC progression by enhancing FA biosynthesis through interacting with ACLY mRNA and provide a novel potential target for HCC therapy.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Non-POU domain-containing octamer binding protein, Fatty acid biosynthesis, ATP-citrate lyase, Insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1
合作部分结果:

合作技术:FISH
原文链接:10.1186/s12935-020-01520-4




