
摘要
Background: Osteosarcoma (OS) is the most common malignant bone tumor and has a poor prognosis. The potential involvement of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in OS progression remains unexplored. Here, we report that CircECE1, a circular RNA derived from human ECE1, plays a critical role in energy metabolism in OS.
Methods: The RIP chip sequence assay was performed to confirm CircECE1, through overexpression or knockdown of CircECE1 to verify its function in 143B and U2OS. RNA immunoprecipitation and immunoprecipitation were used to verify CircECE1's regulation of protein c-Myc and co- immunoprecipitation was used to verified the competitive binding relationship between CircECE1 and SPOP. The influence of CircECE1 on energy metabolism was evaluated by seahorse experiment, western blot, and immunohistochemistry.
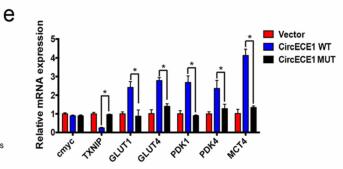
Results: We found that CircECE1 is highly expressed in OS tissues and cells and that CircECE1 knockdown suppresses tumor proliferation and metastasis both in vitro and in vivo. Further, CircECE1 significantly promotes glucose metabolism in OS cells in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, CircECE1 interacts with c-Myc to prevent speckle-type POZ-mediated c-Myc ubiquitination and degradation. C-Myc inhibits thioredoxin binding protein (TXNIP) transcription and subsequently activates the Warburg effect.
Conclusions: CircECE1 regulates the Warburg effect through the c-Myc/TXNIP axis. CircECE1 mediated signal transduction plays a important role in OS process and energy metabolism. These findings may identify novel targets for OS molecular therapy.
Keywords: C-Myc; CircECE1; Glucose metabolism; Osteosarcoma; TXNIP.

伯信合作技术:过表达载体
原文链接:10.1186/s12943-020-01269-4




